热烈祝贺杨自立和罗明副研究员等合作撰写的研究论文“Bienzyme-powered nanorobots with ultrasensitive chemotaxis for precision cancer therapy”被综合性Top期刊National Science Review(2024年IF: 17.1,中科院Q1期刊)接收!
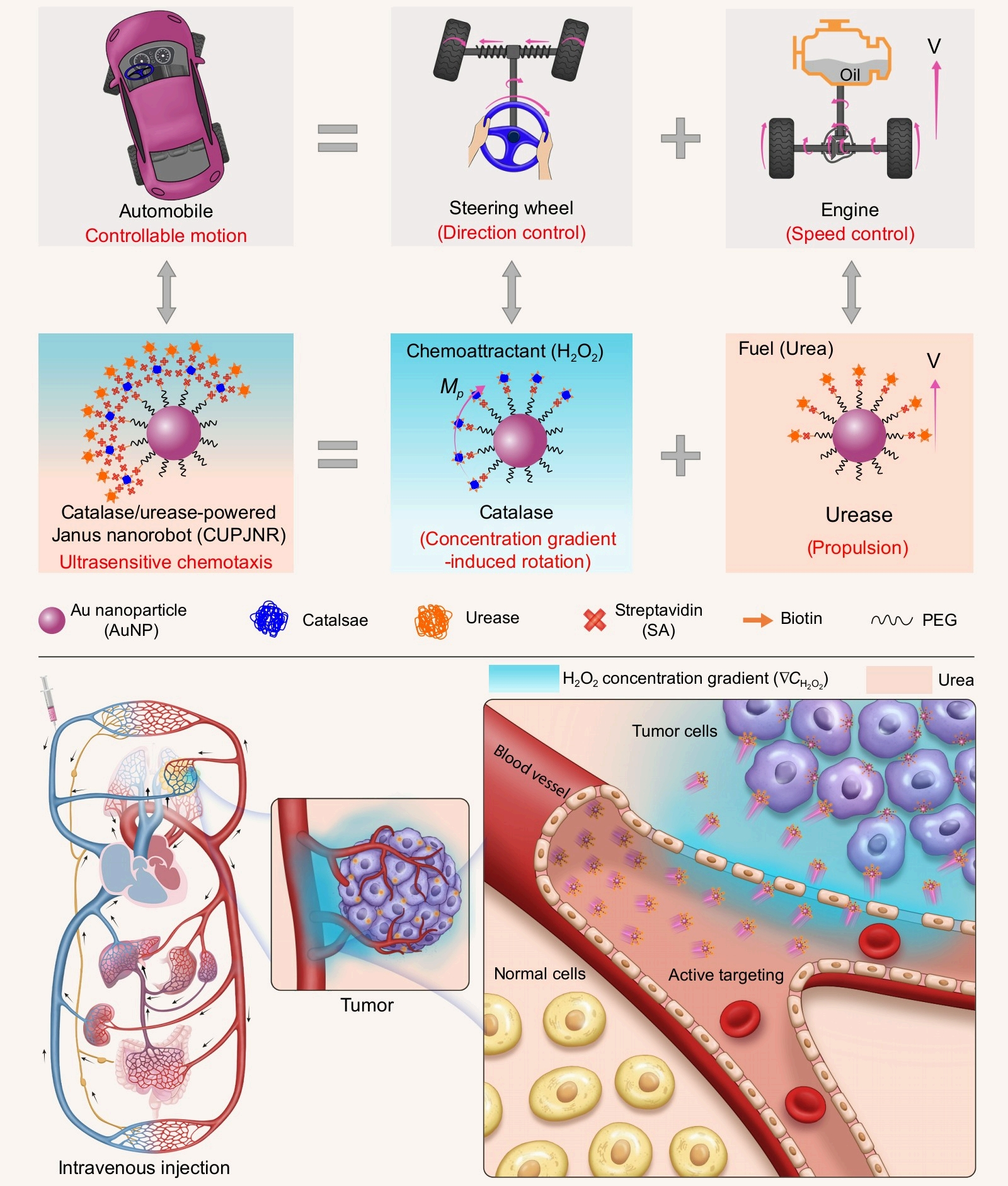
抗肿瘤纳米药物递送系统对肿瘤组织的靶向效率和渗透能力是制约其临床转化的关键瓶颈。本工作报道了一种在单侧表面依次修饰了过氧化氢酶与脲酶的双酶驱动双面神纳米机器人。它们能够以血液循环系统中的内源性尿素与肿瘤过表达的H2O2为燃料,在产生远超平动布朗力的化学驱动力同时还能产生与转动布朗力矩相当的取向力矩,从而能对厘米级距离外的肿瘤组织展现出超灵敏的趋化运动。通过静脉注射进入荷瘤鼠血液循环系统后,双酶驱动纳米机器人能够实现肿瘤组织的高效靶向富集、深层渗透和高效细胞内化。相比于依赖被动扩散的对照组,它们对肿瘤组织的靶向效率提升200倍,渗透能力增强12倍和细胞内化效率提高1970倍。作为药物递送载体,它们能将抗肿瘤药物的抑瘤效果提升49倍。该方法具有通用性,通过更换不同的酶催化部件可制备出应用于不同疾病区域的超灵敏趋化性纳米机器人。这为下一代药物递送系统的构筑提供了全新策略,有望为各类疾病的精准治疗带来颠覆性变革。
原文摘要如下:Low tumor-targeting delivery efficiency (Ɛ) and poor tumor penetration remain critical issues in the clinical translation of nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems. Here we report that bienzyme-powered Janus nanorobots with catalase and urease covering the same hemispheres in sequence demonstrate chemical propulsion far exceeding translational Brownian forces and torques comparable to rotational Brownian torques by leveraging endogenous urea and H₂O₂ gradient in tumor microenvironment, showcasing ultrasensitive chemotaxis toward biomarkers over-expressed by tumor tissues centimeters away and augmented Ɛ. After intravenous injection into a tumor-bearing mouse model, the nanorobots demonstrate significant enhancement in Ɛ, penetration depth, and cell internalization, surpassing those of passive counterparts by 209, >10, and 1970 times, respectively. When loaded with antitumor drugs, they boost the tumor suppression efficacy by approximately 49 times compared with the passive counterparts. This work offers a new strategy for the next-generation drug delivery, promising a paradigm shift for self-propelled nanorobots in precision medicine.