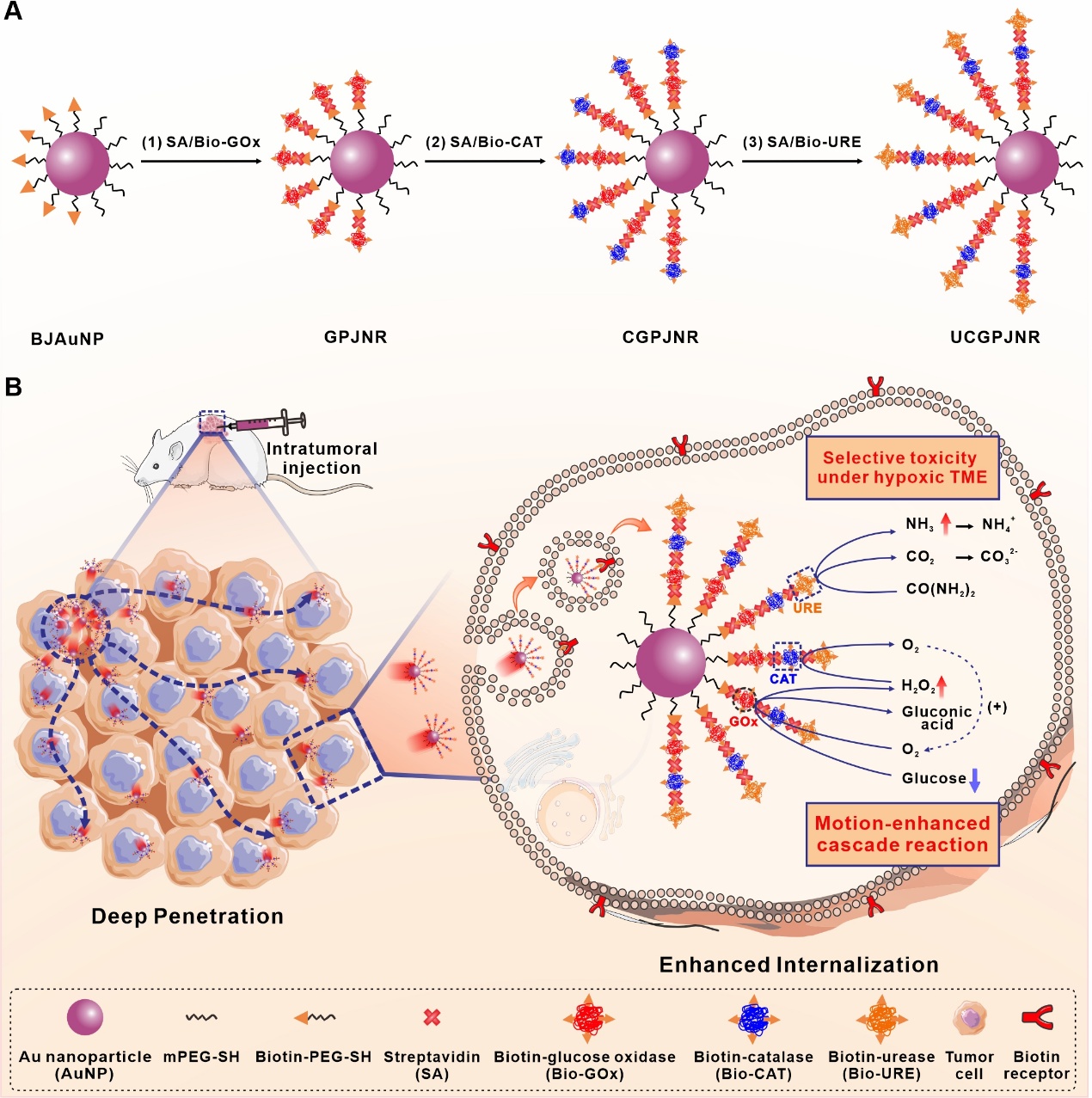
热烈祝贺高志雪和罗明副研究员等撰写的研究论文“Trienzyme-in-one nanoparticle making multifunctional synergistic nanorobot for tumor therapy” 被Wiley出版社旗下专注于微纳尺度技术创新的国际学术期刊Small Methods(2023年IF: 10.7,JCR Q1期刊)接收!当前,基于纳米颗粒的肿瘤药物递送系统仍面临肿瘤内渗透能力不足和细胞内化效率低下的重大挑战。在本研究中,我们通过将葡萄糖氧化酶、过氧化氢酶和脲酶依次整合至生物素修饰的双面神纳米颗粒半表面,构建了一种具备多功能协同效应的纳米机器人。该纳米机器人利用肿瘤微环境中内源性尿素作为燃料,实现高效自主运动,其在肿瘤组织中的渗透深度超过0.55毫米,渗透能力约为基于布朗运动的同类纳米材料的5.5倍。高效运动不仅增强了生物素受体介导的胞吞作用,还加速了内质网/高尔基体通路介导的胞吐过程,显著提升了纳米机器人在肿瘤细胞内的积累与内化效率。在运动过程中释放的氨气可对缺氧肿瘤微环境中的肿瘤细胞产生选择性毒性。此外,纳米机器人通过运动加速葡萄糖氧化酶/过氧化氢酶级联反应,使肿瘤组织中葡萄糖消耗量提高约3倍,从而在大范围内破坏肿瘤细胞代谢。小鼠肿瘤模型实验证明,纳米机器人经瘤内注射后可凭借多重协同机制显著增强肿瘤生长抑制效果。综上所述,本研究提出了一种基于多酶协同修饰的纳米机器人设计策略,为克服肿瘤中的渗透与内化屏障提供了可行路径。
原文摘要如下:Current nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems for tumor therapy face significant challenges in intratumoral penetration and cellular internalization, leading to poor therapeutic efficacy. Herein, we demonstrate that the sequential integration of glucose oxidase (GOx), catalase (CAT) and urease (URE) onto the half surface of biotin-modified Janus nanoparticles via chemical coupling way produces nanorobots of multifunctionality and synergistic effect (denoted as UCGPJNRs). They can autonomously and powerfully move in tumor microenvironment (TME) by using endogenous urea as a fuel, enabling to penetrate deeper than 0.55 mm into tumor tissues, approximately 5.5-fold of the previous counterparts. The UCGPJNRs perform motion-enhanced biotin receptor-mediated endocytosis and endoplasmic reticulum/Golgi apparatus pathway-mediated exocytosis, greatly improving the internalization efficiency of tumor cells. They release NH3 when moving to produce selective toxicity against tumor cells in hypoxic TME. Furthermore, they enhance the glucose consumption by about 3 times due to the motion-accelerated GOx/CAT cascade reaction, disrupting the metabolism against tumor cells on a large area. After intratumorally injected into tumor-bearing mice, UCGPJNRs can significantly amplify the in vivo tumor growth inhibition rate through their synergistic effect. This work provides a plausible strategy to overcome current limitations in tumor treatment by anchoring multiple bioenzymes on one nanoparticle.