热烈祝贺李刚博士和香港中文大学Prof. Yi Long、南洋理工大学A/P. Zhili Dong等合作撰写的综述论文“Thermoresponsive Hydrogels for the Construction of Smart Windows, Sensors, and Actuators”被ACS出版社的期刊Accounts of Materials Research(2023-2024年IF: 14,中科院一区)接收并在线发表(https://doi.org/10.1021/accountsmr.5c00007)!
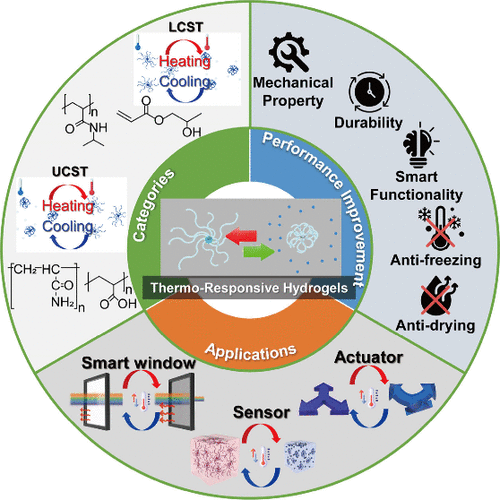
热响应性水凝胶具有根据温度变化自主调节其性能的本征特性,无需外部电源,方便适用于各种环境应用。本文首先建立了热响应性水凝胶中两类热转变,即较低的临界溶解温度(LCST)和较高的临界溶解温度(UCST)的基本科学原理。这些热转变(LCST和UCST)调节热响应性水凝胶在不同环境条件下的响应和变形特性,是控制水凝胶物理特性和反应性的关键决定因素。此外,这些水凝胶集成光子晶体(PC)结构已经成为一种改变介电常数或晶格参数来控制颜色变化的重要方法。由于这些显著的特性,热响应水凝胶在各种智能材料的应用中受到了广泛的关注,包括节能技术、环境和生物识别传感以及控制系统。尽管这些独特的特性推动了智能材料领域的广泛研究,但水凝胶固有的富水成分和受损的机械性能仍然阻碍了它们在极端温度条件下的应用,并容易受到机械应力的影响。为了应对这些挑战,人们设计了创新的策略,包括缠结诱导强化、加入防冻剂和应用多价金属离子,以增强水凝胶的机械鲁棒性,并提高所需的性能指标。
原文摘要如下:Thermoresponsive hydrogels possess an inherent capacity for autonomous adjustment of their properties in response to temperature variations, eliminating the requirement for external power sources and rendering them suitable for diverse environmental applications. Our discourse commences by establishing a foundational comprehension of the two principal categories governing thermal transitions in thermoresponsive hydrogels, namely, the Lower Critical Solution Temperature (LCST) and the Upper Critical Solution Temperature (UCST). These thermal transitions, LCST and UCST, are pivotal determinants of the physical characteristics and reactivity of hydrogels, as they regulate the response and deformations of temperature-sensitive hydrogels across varying environmental conditions. Moreover, the integration of these hydrogels within the photonic crystal (PC) structures has emerged as a notable approach to modulating dielectric constants or lattice configurations, leading to color change. Due to these remarkable properties, thermoresponsive hydrogels have garnered significant research attention for various smart material applications, including energy-saving technologies, environmental and biometric sensing, and control systems. Despite these distinctive features driving extensive research in smart materials areas, challenges persist due to the inherent water-rich composition and compromised mechanical integrity of hydrogels. These limitations impede their deployment in extreme temperature conditions and make them susceptible to mechanical stress. To address these challenges, innovative strategies, including entanglement-induced reinforcement, incorporation of antifreeze agents, and the application of polyvalent metal ions, have been devised to bolster mechanical robustness and enhance the desired performance metrics of hydrogels.