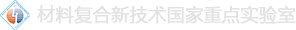
祝贺翟翔祥和罗明副研究员等撰写的研究论文“Photothermal-Drivena-Amylase-ModifiedPolydopamine Pot-Like Nanomotors for Enhancing Penetration and Elimination ofDrug-Resistant Biofilms”被Wiley出版社的著名生物医用材料期刊Advanced Healthcare Materials(2023年IF: 10,SCI Q1期刊)接收!生物酶修饰的抗菌纳米颗粒凭借其能在温和反应条件下实现生物膜降解并促进细菌消除的特性,在根除细菌生物膜感染疾病方面备受关注。然而,现有生物酶修饰的抗菌纳米颗粒在生物膜中的穿透和扩散能力欠佳,导致其难以抵达生物膜深层,使得对生物膜内部细菌的清除效果不佳,极大限制了其在实际治疗中的应用效果。鉴于此,我们在这个工作中通过将α-淀粉酶修饰到聚多巴胺纳米罐状颗粒的外表面发展了一种光热驱动纳米马达。它在808 nm近红外激光照射下,能自主运动到生物膜并通过α-淀粉酶的水解作用高效降解生物膜、进而深入生物膜内部。同时,聚多巴胺特有的生物黏附性使纳米马达能够快速聚集在细菌表面,通过光热效应对深层细菌进行清除。上述协同作用能赋予该纳米马达具有优越的抗生物膜性能,显著加速细菌感染创面的愈合。结合其良好的生物相容性,该光热驱动纳米马达在治疗生物膜相关感染疾病方面具有显著的应用潜力。
原文摘要如下:Biologicalenzyme-functionalized antibacterial nanoparticles, which can degrade biofilmand kill bacteria under mild reaction conditions, have attracted much attentionfor eradicating deep-seated bacterial infections. However, the poor penetrationand diffusion capabilities of recently developed biologicalenzyme-functionalized antibacterial nanoparticles in biofilm severely impairthe eradication efficacy of deep-seated bacteria. Herein, we developed aphotothermal-driven nanomotor (denoted as APPNM) for enhancing the eliminationof drug-resistant biofilms and the eradication of deep-seated bacteria. Thenanomotor contained a pot-like polydopamine (PDA) nanostructure and its outersurface was chemically immobilized with a layer of α-amylases. Under exposureto 808 nm near-infrared (NIR) laser irradiation, the self-propelled nanomotors,integrating the α-amylases to destroy the compact structure of biofilms, canpenetrate deeply into biofilms and effectively eliminate them. Subsequently,they can accumulate on the surface of bacteria using the inherent bio-adhesionproperty of PDA, thereby completely eradicating deep-seated bacteria byphotothermal effect. These synergistic effects enable them to exhibit superiorantibiofilm effects and produce remarkable therapeutic efficacy withaccelerated wound healing in vivo. With the excellent biocompatibility, theas-developed nanomotors have great potential to be applied for treatingbiofilm-related infections.